Clothes Dryer Motor: Role, Components, Types and Efficiency
In the realm of household convenience, the clothes dryer stands as an emblem of modern efficiency. At the heart of this indispensable appliance lies a vital catalyst – the clothes dryer motor. This unassuming yet pivotal component orchestrates the intricate dance of turning damp laundry into warm, dry clothing.
Beyond its functional role, the clothes dryer motor is a dryer part that embodies a convergence of engineering ingenuity and energy-conscious design. In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted world of clothes dryer motors, unveiling their roles, essential components, diverse types, and the pivotal role they play in enhancing energy efficiency.
What Is a Motor?
A motor is a mechanical device designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. It serves as a transformative intermediary, taking in electrical input and generating useful physical movement as output. This transformation is achieved through the interaction of magnetic and electrical forces within the motor’s components.
What Are Clothes Dryer Motors?
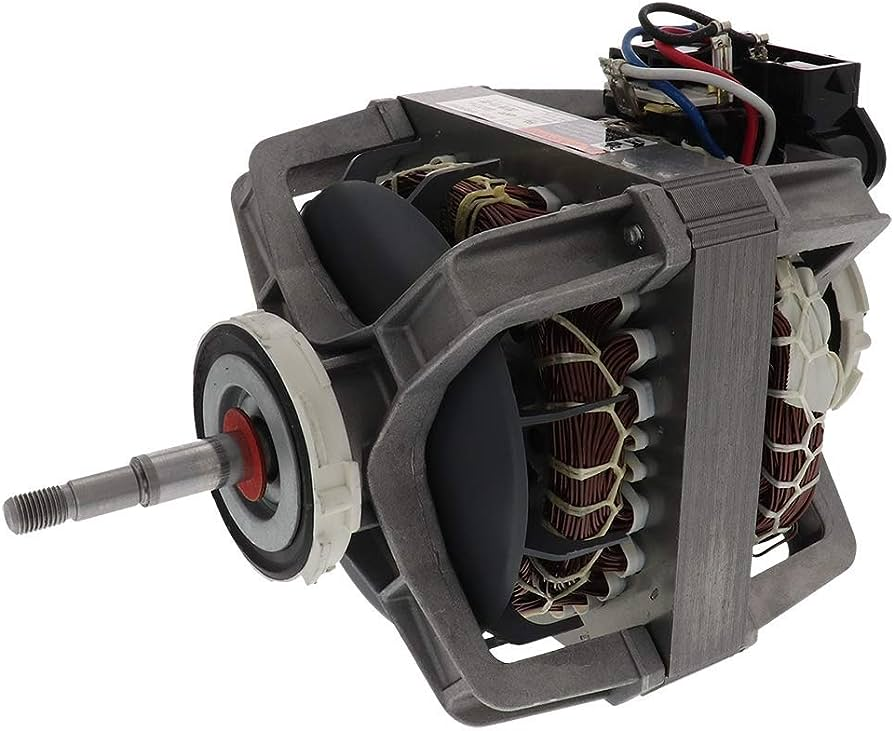
A clothes dryer motor is an electromechanical device responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. Its primary function is to power the rotation of the dryer drum, where wet clothes are tumbled, as well as to drive the blower fan that circulates hot air throughout the drum. This motion and airflow work together to evaporate moisture from the clothes, effectively drying them.
What are the Components of Clothes Dryer Motors?

Inside a clothes dryer motor, a series of intricate components interact seamlessly to produce motion. Key elements include:
1. Motor Core
The motor core serves as the central structural component of the motor assembly. It houses the essential elements that facilitate the motor’s operation, including the rotor and stator.
2. Rotor
The rotor is the moving component of the motor, directly responsible for generating mechanical motion. It consists of a shaft and a set of conductive bars or coils. As electrical current flows through these conductive elements, they interact with the stator’s magnetic field, inducing rotation.
3. Stator
The stator is the stationary component of the motor surrounding the rotor. It comprises a series of electromagnets that produce a rotating magnetic field when energized. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor’s conductive elements, resulting in the rotor’s rotational movement.
4. Fan Blade
In some clothes dryer motors, a fan blade is attached to the rotor shaft. This fan plays a crucial role in promoting air circulation within the dryer drum. As the fan blade rotates, it expels moist air from the drum and facilitates the entry of fresh, dry air, enhancing the drying efficiency.
5. Bearing System
The bearing system supports the rotor shaft, ensuring smooth rotation. There are typically two types of bearings used in clothes dryer motors:
a. Sleeve Bearings
Sleeve bearings are simple bushings that provide support to the rotor shaft. They help reduce friction and enable the shaft to rotate smoothly.
b. Ball Bearings
Ball bearings involve a set of small balls that roll within races to support the shaft. These bearings offer higher efficiency and durability compared to sleeve bearings.
6. Drive Belt or Pulley
In motor-driven clothes dryers, the motor’s rotational motion is transferred to the dryer drum through a drive belt or dryer motor pulley system. This mechanism ensures that the drum rotates, facilitating the tumbling action that promotes even drying.
7. Start Switch
The start switch is a critical element of the motor control system. When the user selects a drying cycle and presses the start button, the start switch activates the motor, initiating the drying process.
8. Centrifugal Switch
Some clothes dryer motors incorporate a centrifugal switch as part of their design. This switch serves to disconnect the start winding from the electrical circuit once the motor reaches a certain speed. This action reduces the load on the start winding during normal operation, preventing damage to the motor.
9. Thermal Overload Protector
Thermal overload protectors are safety features in clothes dryer motors designed to prevent overheating. These protectors monitor the motor’s temperature and disconnect power if the temperature exceeds a safe threshold, safeguarding the motor from potential damage.
10. Wiring and Connectors
The motor assembly is connected to various components of the dryer, such as the power supply and control panel, through a network of wires and connectors. These ensure proper communication and functionality within the dryer system.
By working harmoniously, these components create a functional clothes dryer motor that powers the drum’s rotation, promotes effective air circulation, and contributes to the overall drying process.
What are the Types of Clothes Dryer Motors?
There are several types of clothes dryer motors, each designed to cater to specific needs and functionalities. Here are the main types:
1. Single-Speed Motor
This is the simplest and most common type of clothes dryer motor. It operates at a single fixed speed and is often used in basic dryer models. The motor runs at a constant speed throughout the drying cycle.
2. Multi-Speed Motor
Multi-speed motors offer different speed settings that can be adjusted based on the drying requirements. These motors provide flexibility, allowing users to choose between various drying intensities for different types of fabrics.
3. Variable-Speed Motor
Variable-speed motors are more advanced and offer a wide range of speed options. They can be precisely controlled to adapt to varying drying conditions and fabric types. This type of motor is often found in high-end or technologically advanced dryers.
4. Reversible Motor
Reversible motors have the ability to rotate in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions. This feature is useful for ensuring even drying and preventing tangling of clothes. Reversible motors are particularly common in dryers with a “reverse tumble” function.
5. Induction Motor
Induction motors are known for their reliability and durability. They operate based on electromagnetic induction and are commonly used in dryers due to their ability to provide consistent performance over a long lifespan.
6. Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
Brushless DC motors are efficient and energy-saving options. They offer precise control over speed and direction while reducing energy consumption. BLDC motors are often used in modern, energy-efficient dryer models.
7. Synchronous Motor
Synchronous motors maintain synchronization with the frequency of the power supply. They are known for their precise speed control and are used in applications where accurate timing is crucial, such as in some high-end dryers.
8. Smart Motor
With the rise of smart home technology, some dryers feature smart motors that can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps or integrated into home automation systems. These motors offer advanced features like scheduling, diagnostics, and energy monitoring.
9. Inverter Motor
Inverter motors provide variable speed control by adjusting the voltage and frequency supplied to the motor. This results in smoother and more efficient operation while reducing wear and tear on the motor components.
10. High-Efficiency Motor
High-efficiency motors are designed to minimize energy consumption and optimize drying performance. They incorporate technologies such as improved ventilation and reduced friction to achieve energy savings while maintaining effective drying.
These various types of clothes dryer motors cater to different preferences, efficiency goals, and technological advancements in the laundry appliance industry. The choice of motor type depends on the manufacturer’s design goals and the features desired in the dryer model.
Which types of dryers utilize different types of motors?
This table provides a quick overview of the relationship between different types of dryers and the motors commonly used in each.
| Dryer Type | Commonly Used Motor Types | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Vented Dryers | Single-Speed Motors, Multi-Speed Motors | These basic dryers use simple motors for standard drying cycles. |
| Condenser Dryers | Single-Speed Motors, Multi-Speed Motors, Variable-Speed Motors | These dryers use various motor types to cater to different drying needs. |
| Heat Pump Dryers | Variable-Speed Motors, Inverter Motors, High-Efficiency Motors | Energy-efficient dryers employ motors that match their efficiency goals. |
| Smart Dryers | Smart Motors | Smart dryers integrate advanced features with smart motor technology. |
| Compact Dryers | Single-Speed Motors, Multi-Speed Motors | Motors are tailored for efficient drying in smaller dryer models. |
| Industrial/Commercial Dryers | High-Efficiency Motors, Induction Motors | Durable motors support heavy usage and larger loads in industrial settings. |
| Reversible Tumble Dryers | Reversible Motors | Reversible motors facilitate even drying and prevent clothes tangling. |
| High-End Dryers | Variable-Speed Motors, BLDC Motors, Synchronous Motors | Advanced features are supported by precise and efficient motor types. |
| Gas Dryers | Single-Speed Motors, Multi-Speed Motors | Gas dryers use similar motor types as their electric counterparts. |
Motor Efficiency and Energy Consumption in Clothes Dryers
The efficiency of motors plays a critical role in determining the overall energy consumption of clothes dryers. Efficient motors contribute to reduced energy usage, operational costs, and environmental impact. Here’s a detailed look at how motor efficiency affects energy consumption in clothes dryers, along with measurable measures:
What is the Impact of Motor Efficiency?
Motor efficiency is typically measured as a percentage and represents the ratio of useful mechanical output power to the electrical input power. In the context of clothes dryers, motor efficiency directly influences how effectively the drum rotates and the air circulates within the appliance. High motor efficiency means less energy is wasted, leading to reduced electricity consumption.
What is the Reduced Energy Consumption imn Motors?
An efficient motor significantly reduces the energy required to achieve the same drying performance. For instance:
- Traditional Motor Efficiency: A standard motor might have an efficiency of around 75-80%.
- Efficient Motor Efficiency: Modern efficient motors, such as BLDC or inverter motors, can achieve efficiencies of 85% or more.
This improvement in motor efficiency directly translates to energy savings during each drying cycle.
What are the Energy-Saving Technologies?
Modern clothes dryers are equipped with advanced motor technologies that optimize energy consumption:
1. Brushless DC (BLDC) Motors
BLDC motors offer exceptional efficiency and precise speed control. Compared to traditional motors, BLDC motors can provide:
- Efficiency Boost: BLDC motors can achieve efficiency levels of up to 90% or more.
- Energy Savings: They can save around 30-40% more energy compared to older motor designs.
2. Inverter Motors
Inverter motors provide variable speed control, adjusting their speed based on drying conditions:
- Adaptive Performance: Inverter motors can adjust speed and energy consumption according to the load and moisture content.
- Energy Savings: They can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to fixed-speed motors.
3. High-Efficiency Motors
High-efficiency motors optimize energy usage through reduced heat generation and energy losses:
- Efficient Design: These motors are engineered to operate with minimal wasted energy.
- Energy Savings: They can achieve energy savings of around 15-20% compared to standard motors.
What is the Importance of Proper Maintenance?
Regular maintenance enhances motor efficiency and reduces energy consumption:
- Clean Filters: Ensuring lint filters are clean reduces motor strain and improves overall efficiency.
- Proper Ventilation: Adequate ventilation prevents overheating and ensures motors work optimally.
- Component Care: Regular inspection of motor components prevents energy losses due to wear and tear.
Troubleshooting Motor Problems
Recognizing signs of motor malfunction or failure is crucial to preventing potential issues and hazards. If you notice excessive vibrations, unusual noises, or if the dryer fails to start altogether, it’s a clear indication that the motor might be facing problems. To troubleshoot minor motor-related issues, follow these steps:
- Check Power Supply: Ensure that the dryer is properly plugged in and receiving power.
- Inspect Belts and Pulleys: Examine the belts and pulleys that connect the motor to the drum. Damaged or loose components could affect motor operation.
- Clean and Ventilate: Dust and lint accumulation can hinder motor performance. Regularly clean the motor area and ensure proper ventilation.
- Avoid DIY Repairs: While minor issues can be resolved through simple troubleshooting, complex motor problems should be handled by professionals to prevent safety risks.
Upgrading and Replacing Motors
As your clothes dryer ages, you might face the decision of whether to repair or replace a malfunctioning motor. Factors such as the cost of repair, the age of the appliance, and the availability of replacement parts come into play. Upgrading to a more efficient motor can significantly enhance the dryer’s overall performance and energy savings. When considering a replacement motor:
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the replacement motor matches the specifications of your dryer model.
- Consult Professionals: Seek advice from appliance technicians to guide your decision between repair and replacement.
- Consider Efficiency: Upgrading to a more energy-efficient motor might lead to long-term savings on utility bills.
FAQ Dryer Motor
How do I know if my dryer motor is bad?
If your dryer isn’t starting, makes unusual noises, or has a burning smell, your motor might be bad. Another sign is the drum not turning even when the dryer is on. You can also check for continuity using a multimeter or consult a professional for a diagnosis.
How much does it cost to replace a dryer motor?
The cost of replacing a dryer motor varies depending on the brand, model, and whether you hire a technician. On average, motor replacement costs can range from $100 to $300. It’s recommended to get quotes from repair services for an accurate estimate.
What kind of motor do dryers have?
Dryers commonly have various types of motors, including single-speed, multi-speed, variable-speed, and high-efficiency motors. Modern dryers may feature brushless DC (BLDC) motors, inverter motors, or even smart motors for advanced functionality.
What causes a motor to go out in a dryer?
Several factors can lead to a dryer motor failing:
1. Overheating due to blocked vents or excessive lint buildup.
2. Wear and tear from continuous use.
3. Electrical issues, like voltage fluctuations or power surges.
4. Component failure within the motor, such as bearings or windings.
Conclusion
The clothes dryer motor, a silent workhorse, plays a vital role in our daily lives. Its efficiency impacts both our convenience and our ecological footprint. Understanding its inner workings, recognizing signs of trouble, and implementing regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of the motor and the dryer as a whole.
As we look ahead, the ever-evolving landscape of dryer motor technology promises more efficient, intuitive, and sustainable solutions that will further streamline our laundry routines while contributing to a greener future. Stay tuned for the next blog post installment, where we’ll conclude our exploration of the fascinating world of clothes dryer motors







